Porsche and the Technical University of Cluj-Napoca in Romania have unveiled a groundbreaking innovation that could redefine the future of internal combustion engines: the six-stroke engine. This cutting-edge technology, detailed in a patent filed on September 12, 2024, aims to combine the power density of two-stroke engines with the environmental cleanliness of four-stroke designs, promising a revolutionary leap in engine performance and efficiency.
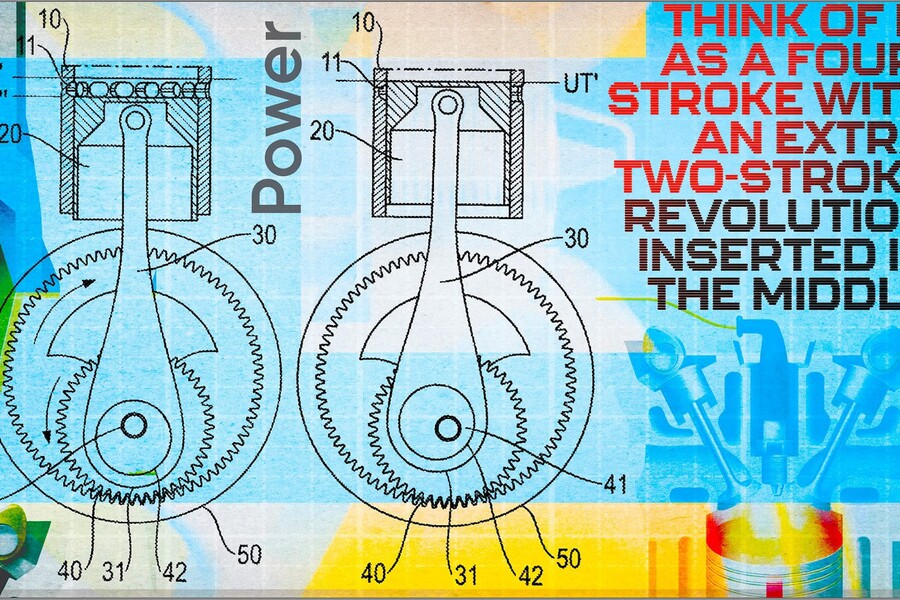
The six-stroke engine operates on a unique principle that incorporates two consecutive power strokes, bracketed by conventional intake-compression and exhaust strokes. Unlike traditional engines, where a piston completes four strokes in two crankshaft revolutions, the six-stroke engine requires three revolutions to achieve its cycle. This design introduces an additional power stroke by utilizing scavenging ports at the cylinder’s lowest point, allowing fresh air to force out exhaust gases before compressing the next charge. The result is a smoother engine with enhanced power delivery and potentially lower emissions.
The innovation stems from a sophisticated crankshaft design. Instead of connecting rods attaching directly to the crankshaft, they are linked to a complex assembly involving planet wheels and annulus gears. This configuration allows the piston to achieve two distinct top-dead-center positions and one extended bottom-dead-center position. The intricate mechanism enables precise control of the combustion process, enhancing efficiency and performance. Additionally, the design incorporates a variable-compression feature, adjusting the crankshaft geometry to optimize compression ratios for various operating conditions.
The six-stroke engine’s potential benefits are vast. The additional power stroke promises a significant increase in specific output, making engines more powerful without increasing size or cylinder count. For instance, an inline-six configuration in a six-stroke setup could rival the smoothness of a V-12 engine. This could have implications for a wide range of applications, from high-performance sports cars to compact, efficient range-extender engines for hybrid vehicles. Moreover, the engine’s smoother operation could reduce vibration and noise, enhancing the driving experience.
Despite its promise, the six-stroke engine faces considerable challenges. The complex crankshaft design poses significant manufacturing and assembly hurdles. Lubrication is another concern, as the intricate components demand precise oil flow to minimize friction and wear. Furthermore, the need for scavenging ports introduces potential emissions issues, as trace amounts of lubricating oil could mix with exhaust gases. Addressing these challenges will be critical to making the six-stroke engine viable for mass production.
The innovative concept has garnered attention from automotive enthusiasts and engineers alike. While Porsche and its Romanian collaborators have not disclosed specific performance metrics or production timelines, the engine’s potential to bridge the gap between power and efficiency has sparked widespread interest. Industry experts note that the technology could provide an intermediate solution as the automotive sector transitions towards electrification.
The six-stroke engine’s prospects remain uncertain, given the technical and economic hurdles it must overcome. However, the involvement of a prestigious manufacturer like Porsche lends credibility to the project. The engine represents a bold attempt to push the boundaries of internal combustion technology, showcasing the ingenuity and determination of its creators.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, innovations like the six-stroke engine highlight the ongoing relevance of internal combustion technology. While electric and hydrogen-powered vehicles dominate discussions about the future of mobility, breakthroughs in traditional engine designs remind us that there is still room for improvement and innovation in established technologies. The six-stroke engine may not yet be ready for the road, but it stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of progress in engineering.